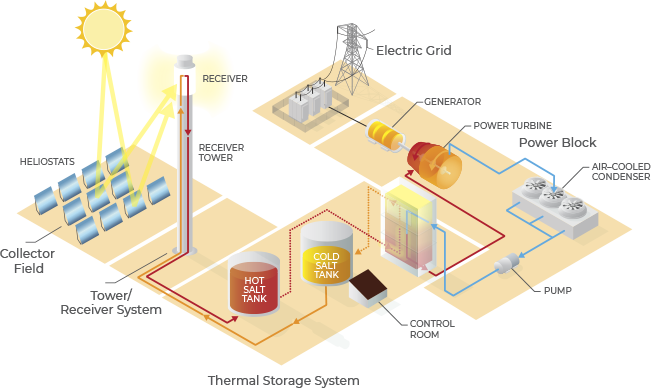
The process of producing power from the sun’s radiation involves several steps. Firstly, the concentrating mirrors focus the solar radiation onto the receiver to heat up a heat transfer fluid to high temperatures. In the case of tower technology, molten salts are typically used as the heat transfer fluid. The same molten salts, stored in large tanks, are also used as the thermal energy storage medium.
In order to produce power, the hot salts are withdrawn from the storage tank and are made to circulate through a series of heat exchangers where they generate steam by heating up water. The pressurised steam is what drives the steam turbine and this rotational motion is then converted into electrical power in the generator. The cool steam from the turbine is then condensed into water in an air-cooled condenser, recompressed and pumped back into the salt/water heat exchangers.